Note
Click here to download the full example code
Tutorial 0: Preparing your data for gradient analysis¶
In this example, we will introduce how to preprocess raw MRI data and how to prepare it for subsequent gradient analysis in the next tutorials.
Requirements¶
For this tutorial, you will need to install the Python package
nilearn version 0.9.0 or above. You can
do it using pip:
pip install "nilearn>=0.9.0"
Preprocessing¶
Begin with an MRI dataset that is organized in BIDS format. We recommend preprocessing your data using fmriprep, as described below, but any preprocessing pipeline will work.
Following is example code to run fmriprep using docker from the command line:
docker run -ti --rm \
-v <local_BIDS_data_dir>:/data:ro \
-v <local_output_dir>:/out poldracklab/fmriprep:latest \
--output-spaces fsaverage5 \
--fs-license-file license.txt \
/data /out participant
Note
For this tutorial, it is crucial to output the data onto a cortical surface template space.
Import the dataset as timeseries¶
The timeseries should be a numpy array with the dimensions: nodes x timepoints
Following is an example for reading in data:
import nibabel as nib
import numpy as np
filename = 'filename.{}.mgz' # where {} will be replaced with 'lh' and 'rh'
timeseries = [None] * 2
for i, h in enumerate(['lh', 'rh']):
timeseries[i] = nib.load(filename.format(h)).get_fdata().squeeze()
timeseries = np.vstack(timeseries)
As a working example, simply fetch timeseries:
from brainspace.datasets import fetch_timeseries_preprocessing
timeseries = fetch_timeseries_preprocessing()
Confound regression¶
To remove confound regressors from the output of the fmriprep pipeline, first extract the confound columns. For example:
from nilearn.interfaces.fmriprep import load_confounds_strategy
confounds_out = load_confounds_strategy("path/to/fmriprep/output/sub-<subject>_task-<task>_space-<space>_desc-preproc_bold.nii.gz",
denoise_strategy='simple')
As a working example, simply read in confounds
from brainspace.datasets import load_confounds_preprocessing
confounds_out = load_confounds_preprocessing()
Do the confound regression
from nilearn import signal
clean_ts = signal.clean(timeseries.T, confounds=confounds_out).T
And extract the cleaned timeseries onto a set of labels
import numpy as np
from nilearn import datasets
from brainspace.utils.parcellation import reduce_by_labels
# Fetch surface atlas
atlas = datasets.fetch_atlas_surf_destrieux()
# Remove non-cortex regions
regions = atlas['labels'].copy()
masked_regions = [b'Medial_wall', b'Unknown']
masked_labels = [regions.index(r) for r in masked_regions]
for r in masked_regions:
regions.remove(r)
# Build Destrieux parcellation and mask
labeling = np.concatenate([atlas['map_left'], atlas['map_right']])
mask = ~np.isin(labeling, masked_labels)
# Distinct labels for left and right hemispheres
lab_lh = atlas['map_left']
labeling[lab_lh.size:] += lab_lh.max() + 1
# extract mean timeseries for each label
seed_ts = reduce_by_labels(clean_ts[mask], labeling[mask], axis=1, red_op='mean')
Out:
/home/oualid/Apps/anaconda3/envs/py3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/nilearn/datasets/__init__.py:89: FutureWarning: Fetchers from the nilearn.datasets module will be updated in version 0.9 to return python strings instead of bytes and Pandas dataframes instead of Numpy arrays.
"Numpy arrays.", FutureWarning)
Dataset created in /home/oualid/nilearn_data/destrieux_surface
Downloading data from https://www.nitrc.org/frs/download.php/9343/lh.aparc.a2009s.annot ...
...done. (0 seconds, 0 min)
Downloading data from https://www.nitrc.org/frs/download.php/9342/rh.aparc.a2009s.annot ...
...done. (0 seconds, 0 min)
Calculate functional connectivity matrix¶
The following example uses nilearn:
from nilearn.connectome import ConnectivityMeasure
correlation_measure = ConnectivityMeasure(kind='correlation')
correlation_matrix = correlation_measure.fit_transform([seed_ts.T])[0]
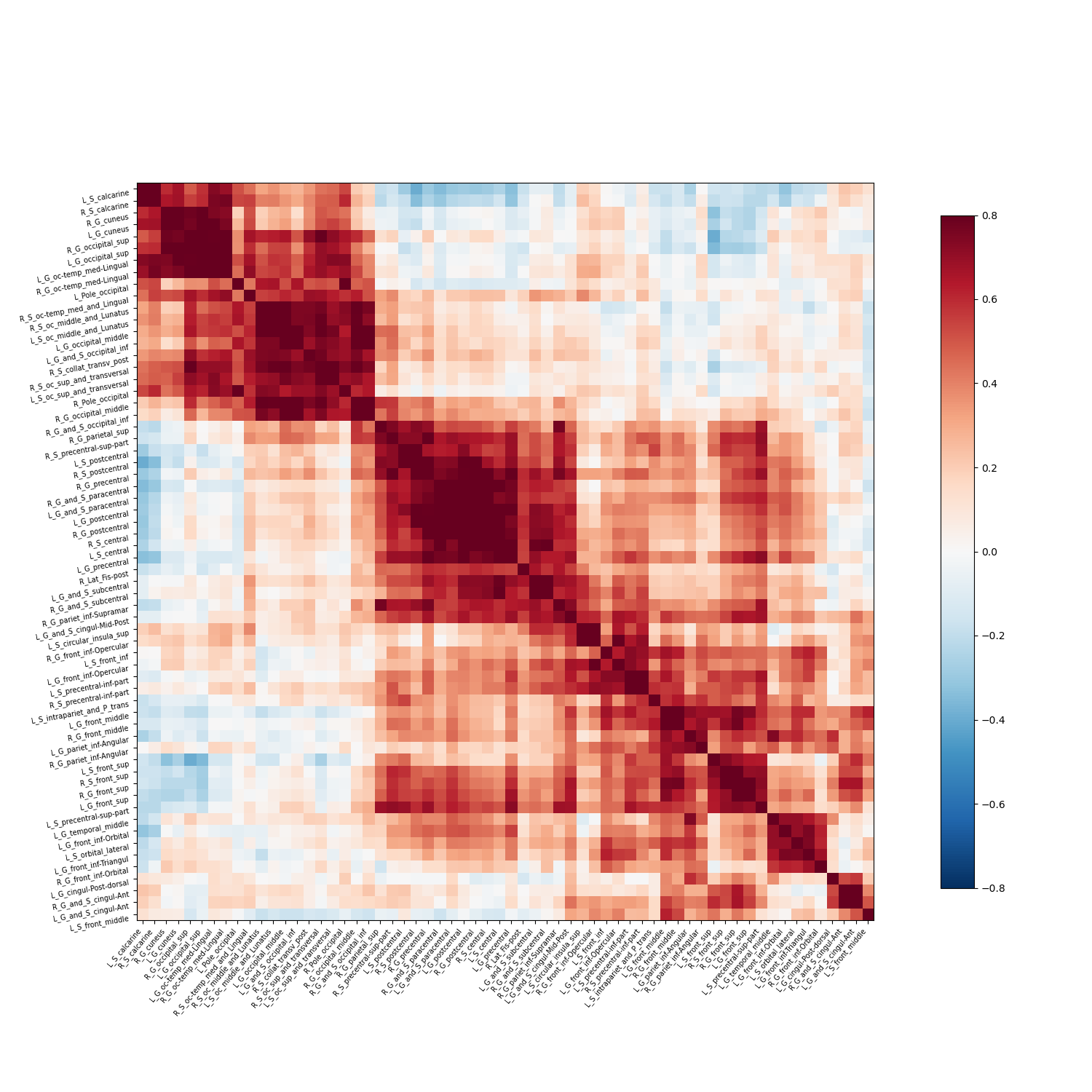
Plot the correlation matrix:
from nilearn import plotting
# Reduce matrix size, only for visualization purposes
mat_mask = np.where(np.std(correlation_matrix, axis=1) > 0.2)[0]
c = correlation_matrix[mat_mask][:, mat_mask]
# Create corresponding region names
regions_list = ['%s_%s' % (h, r.decode()) for h in ['L', 'R'] for r in regions]
masked_regions = [regions_list[i] for i in mat_mask]
corr_plot = plotting.plot_matrix(c, figure=(15, 15), labels=masked_regions,
vmax=0.8, vmin=-0.8, reorder=True)
Run gradient analysis and visualize¶
Run gradient analysis
from brainspace.gradient import GradientMaps
gm = GradientMaps(n_components=2, random_state=0)
gm.fit(correlation_matrix)
Out:
GradientMaps(n_components=2, random_state=0)
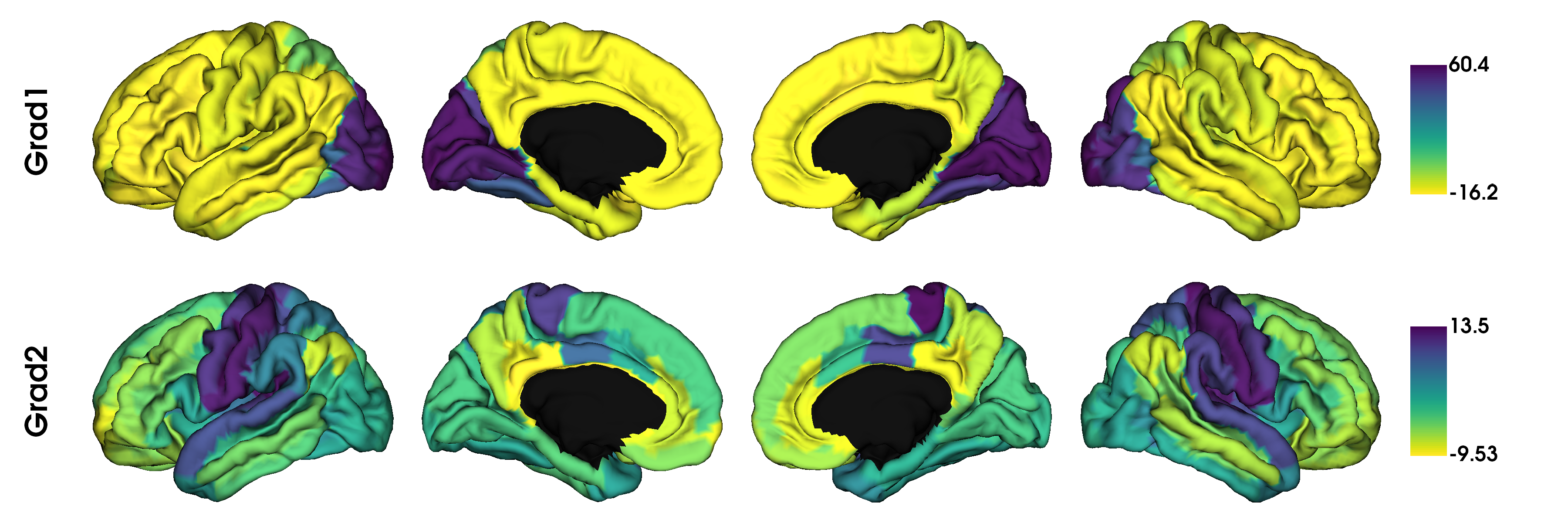
Visualize results
from brainspace.datasets import load_fsa5
from brainspace.plotting import plot_hemispheres
from brainspace.utils.parcellation import map_to_labels
# Map gradients to original parcels
grad = [None] * 2
for i, g in enumerate(gm.gradients_.T):
grad[i] = map_to_labels(g, labeling, mask=mask, fill=np.nan)
# Load fsaverage5 surfaces
surf_lh, surf_rh = load_fsa5()
plot_hemispheres(surf_lh, surf_rh, array_name=grad, size=(1200, 400), cmap='viridis_r',
color_bar=True, label_text=['Grad1', 'Grad2'], zoom=1.5)
This concludes the setup tutorial. The following tutorials can be run using either the output generated here or the example data.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 3.871 seconds)